A solute is any substance that gets dissolved in a solution. And a solvent is any material that dissolves the solute.
The primary difference between the solute and solvent is that solute is the minor component of a solution. In contrast, the solvent is the major component of a solution that dissolves solute to create a solution.
Solute and solvent are the two most widely used terms in chemistry and, indeed, the most confusing ones. Chemistry students would agree. However, understanding the key differences between these substances can help sort out the solute-solvent confusion.
Table of Contents
What is a Solute?
Every solution is a homogenous mixture of various substances, one of which is a solute. A solute is any substance dissolved in a solution whose proportion is always less than the solvent. A solute dissolves within a solvent.
Furthermore, the solute particles aren’t usually visible to the naked eye. They can’t be separated from the solution by mechanical methods.
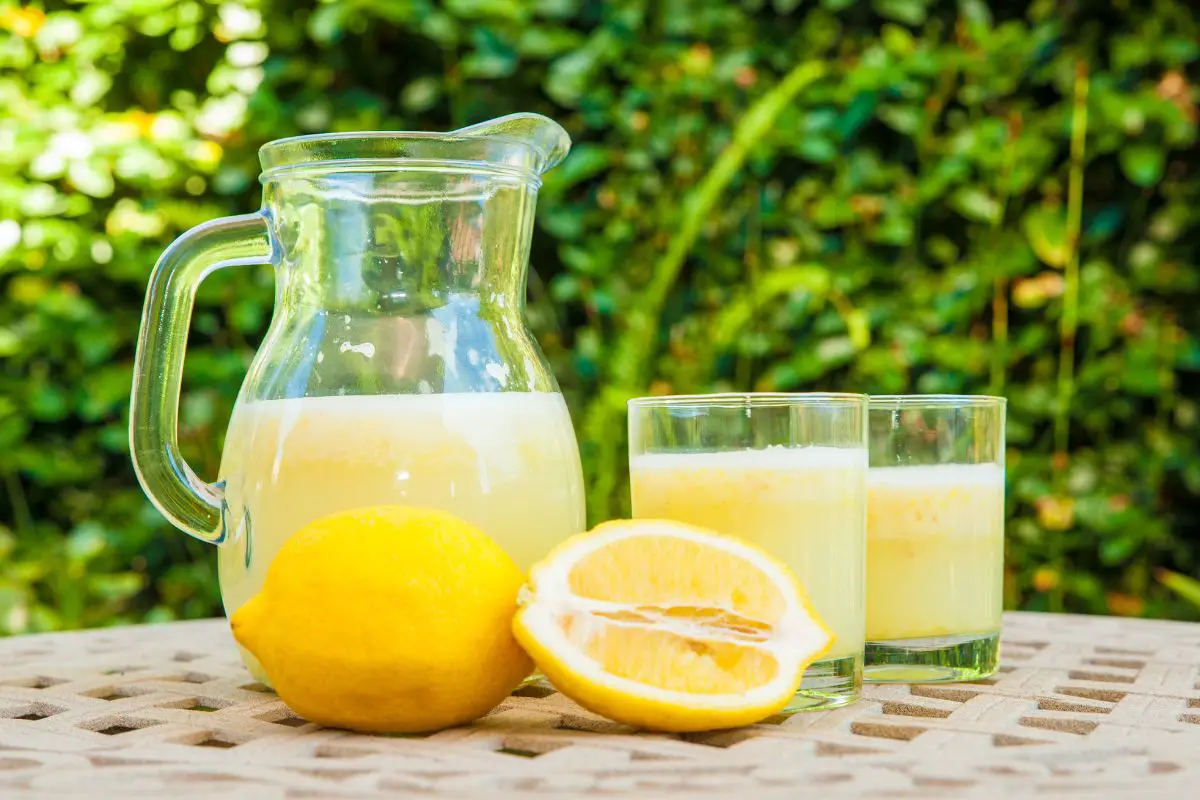
Example of Solutes
For example, consider sipping chilled lemonade. In this lemonade example, sugar and lemon juice are the two solutes. You can’t separate the lemon juice and dissolved sugar by any means.
Note: Solutes in the solution are estimated by their concentration, which is the amount of solute divided by the total volume of the solution.
The property of solutes to be able to dissolve in a solvent is defined as its solubility.

Different Types of Solutes
There are different types of solutes – gas, liquid, and solid.
- A gaseous solute can only be dissolved in gas, liquid, and solid solvents.
- A liquid and solid solute can only be dissolved in liquid and solid solvents.
What is a Solvent?
A solvent is the other major part of the solution. A solvent is derived from the Latin word solv which means “to loosen.”
The solvent is the substance in which a solute is dissolved to make a solution. Solvents are generally liquid but can also be a solid, gas, or supercritical fluid (SCF.)
Unlike solutes, the amount of solvent is greater than the solute.

Examples of Solvents
For example, in the previous lemonade example, water is the solvent. Its amount will always be greater than the solutes, which are sugar and lemon juice.
Note: Water is a universal solvent because it can dissolve almost every solute better than any other liquid. Also, because of its polarity, water is the best solvent.
Polarity
There are two types of solvents based on polar and nonpolar. Polarity is the ability of a solvent to dissolve any solute.
- Water is a polar solvent.
- Carbon tetrachloride and benzene are two common nonpolar solvents.
Organic vs Inorganic
Again, solvents are also categorized based on their chemical composition: organic or inorganic.
Some organic solvents are gasoline, benzene, toluene, acetone, ethanol, and hexane. On the other hand, liquid anhydrous ammonia, sulfuric acid, and sulfuryl chloride fluoride are some inorganic solvents.
Solute vs Solvent
| Solute | vs | Solvent |
| A solute is a substance that is dissolved in a solvent | Definition | A solvent is a substance that dissolves the solute |
| Higher than solvent | Boiling Point | Lower than solute |
| Solid, liquid, or gas | Physical State | Liquid or gas |
| It depends on the properties of the solute | Dependability | It depends on the properties of the solvent |
| Less than solvent | Quantity In The Solution | More than solute |
| It depends on the surface area and size of the molecules | Solubility | It depends on its properties, like its polarity |
| Heat is transferred to the solute | Heat Transfer | Heat is transferred from the solvent |
Solute vs Solvent – Key Differences Explained
Here are some brief and significant differences between the two major parts of the solution.
Definition
A solute is a substance dissolved in a solvent to create a solution. In contrast, a solvent is a material that dissolves solute to create a solution.
Boiling Point
The boiling point of a solvent and solute is essential to consider. Solutes have a higher boiling point than solvents. This is because solutes require higher temperatures to dissolve into the solvent fully.
Physical State
The solute can exist in a solid, liquid, or gaseous state. On the other hand, a solvent mainly exists in liquid form. But some gaseous solvents are also there.
Example of Solvents
For example, water (solute) in the air (solvent.) Acetic acid is a common solvent used to make key components found in wood glue, synthetic fibers, and fabrics.
Quantity in a Solution
The amount of solute is always less than the solvent in a solution. In contrast, the amount of solvent is more than the solute in a solution.
Solubility
A solute’s solubility depends on its properties, like the surface area and size of molecules.
On the other hand, the solubility of a solvent depends on its properties, like its polarity.
Heat Transfer
Heat is transferred to the solute and from the solvent in a solution.
The fundamental difference between solute and solvent is that solute is anything that dissolves, and the solvent is the dissolving medium.