The main difference between accuracy and precision is that accuracy refers to the closeness of the measured value to the accepted value (or true value). On the other hand, precision refers to how close measurements of the same item are to each other.
Accuracy and precision are two important terms often used in measurement systems. These are used to represent the measuring ability of an instrument.
Table of Contents
Difference Between Accuracy and Precision
| Accuracy | vs. | Precision |
| Checks the closeness of the experimental value with the standard value | Meaning | Checks how consistent the obtained experimental values are |
| One factor for measurement | Method of Measurement | Multiple factors for measurement |
| Accurate values have to be precise most of the time | Mutual Relationship | Precise values may or may not be accurate |
| Accuracy is affected by systematic error | Which Error Affects The Value? | Precision is affected by random errors or observational errors |
What is Accuracy?
Accuracy measures correctness. In mathematics, science, and engineering, the definition of accuracy is the closeness of a measurement to the true value.
The nearer the measured value to the actual value, the higher the accuracy. The farther the measured value from the actual value, the lower the accuracy.
According to ISO (International Organization for Standardization), the term accuracy describes measurement with both accurate and consistent results. ISO also says that an accurate measurement has no error.
A systematic error is an error that is not determined by chance but introduced by an inaccuracy inherent in the system.
Examples of Accuracy
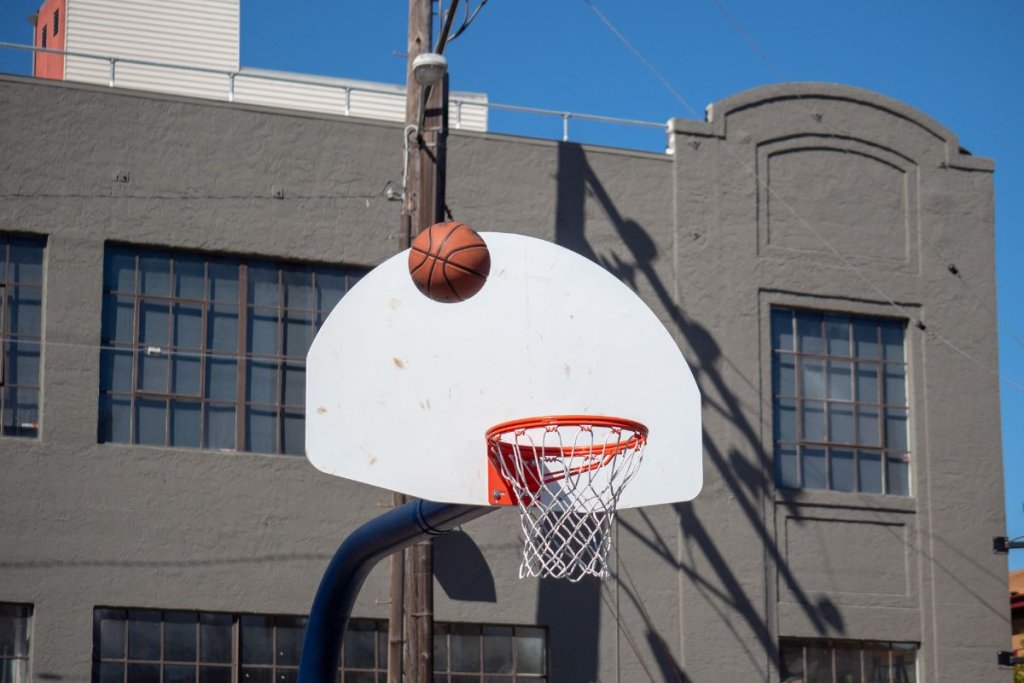
- Accuracy is how close your ball gets to your target: the basket when you repeatedly throw a basketball intending to pass the ball through the basket.
- A dart that hits the bull’s eye is an example of high accuracy.
- Suppose the correct answer to a problem is 3 or 5, and the students got 3, 3.2, 3.5, 2.9, and 2.95. In that case, you can say there is accuracy in their answer because the values are all close to 3, which is the correct answer.
However, suppose the correct answer is seven, one person gets 6.9, and the others get much higher or lower values. In that case, the student who got 6.9 is more accurate.
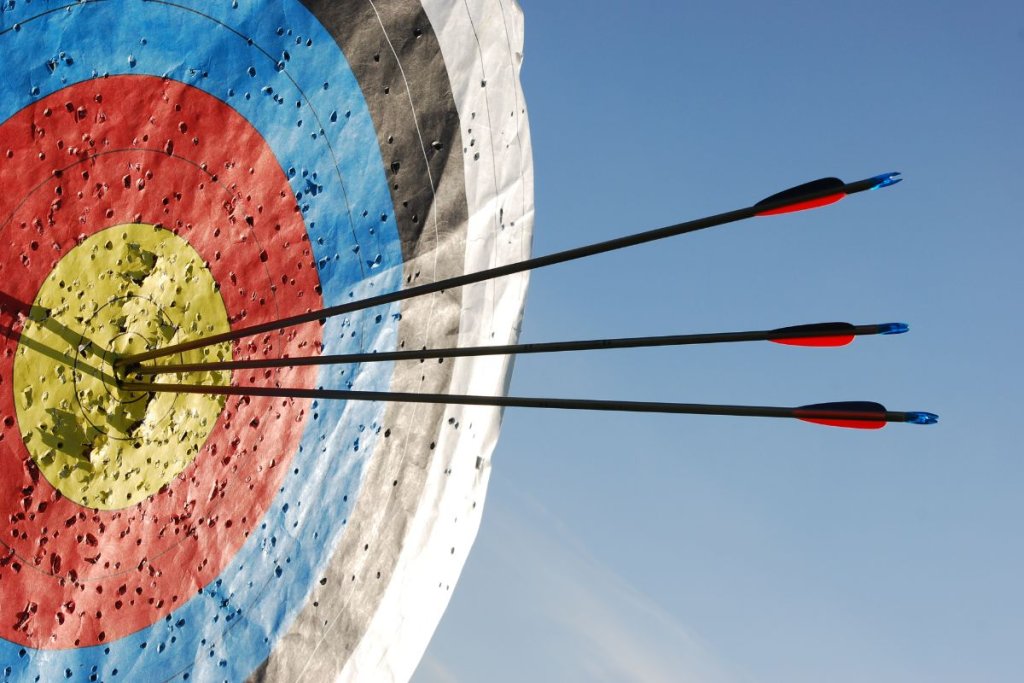

What is Precision?
Precision measures exactness and refers to the degree of uniformity or repeatability in measurements. When measurements are repeated, precision shows consistency in the results obtained.
Whether the measured value is close to the actual value or not, consistency matters. The less the difference is among the values obtained, the more precise it is.
Why Measure Precision?
The motive of precision is to determine whether you obtain the same value under similar or different specified conditions. When the variation between the values is limited, the precision is high.
Precise values differ from each other due to random observational errors.
Instruments that generate differences in value when operated under the same environmental conditions by the same user are termed low-precision instruments. It happens due to the breakage of parts or other issues.
Also, instruments show significant differences under different conditions like temperature and humidity. Accuaracy depends on precision because accurate values should be precise.
Examples of Precision
- When you repeatedly throw a basketball intending to pass the ball through the basket, precision is when you continue to hit the same spot often, which may not necessarily be the basket.
- If the correct answer to a problem is 3, and 5 students each got 6, 6.1, 5.8, 7 and 5. The values are precise or close to each other but not accurate as they cannot be compared to 3, which is the correct answer.

Use the Correct Measurement
Accuracy and precision are crucial for measuring scientific data, and both represent how near a measured value is to an expected value.
Accuracy represents the closeness of the value to the true value. In contrast, precision means how reproducible experimental values are, even if they are far from the standard value.
Quick Trick to Remember the Difference
- ACcurate is Correct (or Close to real value)
- PRecise is Repeating (or Repeatable)
If you’ve enjoyed this article, check out our post on quantitative versus qualitative data.